The conversion of mechanical energy to electrical energy is a topic of great interest, as it involves transforming day-to-day activities into useful forms of energy, and researchers are continually seeking new methods for this conversion.
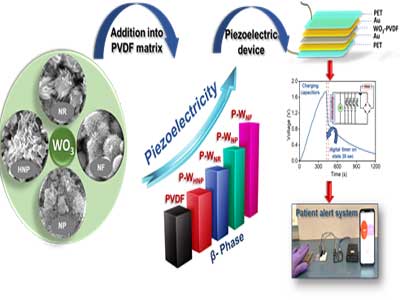
An innovative piezoelectric device was fabricated using a polymer nanocomposite of flower-shaped tungsten trioxide nanomaterial embedded in a polyvinylidene fluoride matrix, paving a viable path towards flexible, wearable, highly efficient, energy-harvesting, pressure-sensing devices.
Read in Hindi: पहनने योग्य स्वास्थ्य निगरानी प्रणालियों के सुधार में मिली नई सफलता
The high sensitivity and energy efficiency of this nano-engineered system make it ideal for biomedical uses. In particular, it can be incorporated into wearable health monitoring systems that can capture biomechanical energy from minor to major body movements like heartbeats, pulses, breathing, walking, etc., and transform it into electrical signals. By using these signals, physiological parameters can be monitored in real time without requiring external power sources.
Researchers at the Centre for Nano and Soft Matter Sciences in Bengaluru, an autonomous institute of the Department of Science and Technology, employed a systematic experimental approach to explore the interactions between polymers and nanomaterials.
They used the same nanofiller to trace their interactions with varying morphologies, crystal structures, and surface charges. Out of the four dissimilar morphologies examined, the nanoflowers characterised by a crystal system with three axes of unequal length and three unequal angles and the highest surface charge demonstrated the most effective interaction with the PVDF matrix, leading to the highest piezoelectric phase.
To further enhance energy generation, an optimisation process was carried out to determine the ideal nanofiller concentration within the PVDF matrix. This involved the fabrication and testing of self-powered energy-harvesting devices.
The research, which involves mixing flexible piezoelectric polymer and nanoparticles and a systematic study of the resultant mechanical energy conversion efficiency, gives insight into understanding what type of nanoparticle can enhance the piezoelectric properties of a piezoelectric polymer.
This study, published in ACS Applied Electronic Materials, also demonstrated the possibility of using this prototype for real-time biomedical applications, particularly in patient monitoring.
The research by the team, Ankur Verma, Pritha Dutta, Nilay Awasthi, Dr Ashutosh K Singh, and Dr CK Subash, is an important step towards intelligent, compact, and sustainable healthcare technologies and opens doors for more widespread uses in energy harvesting and smart textiles. The CeNS team foresees that such cutting-edge nanocomposite-based devices will significantly contribute to the growing demand for next-generation biomedical wearables.















Related Items
Transforming India into a ‘Global Biopharma Hub’…
The Great Urban Predicament: India's Catch-22…
Big breakthrough in rare-earth magnetism...