From 2005 to 2015, surface melt off ice caps and glaciers of the Queen Elizabeth Islands grew by an astonishing 900 percent, from an average of three gigatons to 30 gigatons per year, according to results published today in the journal Environmental Research Letters.
“In the past decade, as air temperatures have warmed, surface melt has increased dramatically,” said lead author Romain Millan, an Earth system science doctoral student.
 The team found that in the past decade, overall ice mass declined markedly, turning the region into a major contributor to sea level change. Canada holds 25 percent of all Arctic ice, second only to Greenland.
The team found that in the past decade, overall ice mass declined markedly, turning the region into a major contributor to sea level change. Canada holds 25 percent of all Arctic ice, second only to Greenland.
The study provides the first long-term analysis of ice flow to the ocean, from 1991 to 2015.
The Canadian ice cap has glaciers on the move into the Arctic Ocean, Baffin Bay and Nares Strait. The researchers used satellite data and a regional climate model to tally the “balance” of total gain and loss each year, and the reasons why. Because of the huge number of glaciers terminating in area marine basins, they expected that discharge into the sea caused by tide water hitting approaching glacier fronts would be the primary cause.
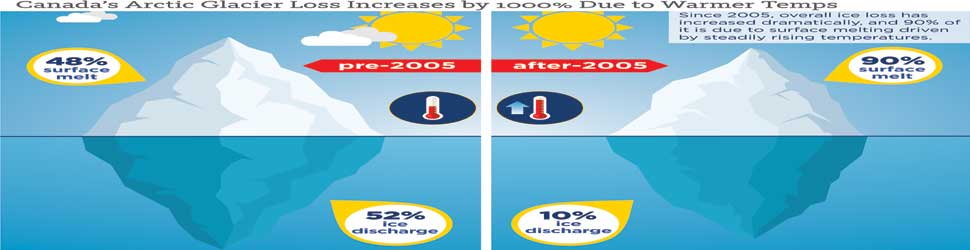
In fact, they determined that until 2005, the ice loss was caused about equally by two factors: calving icebergs from glacier fronts into the ocean accounted for 52 percent, and melting on glacier surfaces exposed to air contributed 48 percent. But since then, as atmospheric temperatures have steadily climbed, surface melt now accounts for 90 percent.
Millan said that in recent years ice discharge was only a major component in a few basins, and that even rapid, short term increases from these ice fields only had a minor impact on the long-term trend.
Millan added, “We identified meltwater runoff as the major contributor to these ice fields’ mass loss in recent years. With the ongoing, sustained and rapid warming of the high Arctic, the mass loss of the Queen Elizabeth Islands area is likely to continue to increase significantly in coming decades.”















Related Items
How the winds of change reached a small shop…
AI reveals importance of rooftops in climate change fight
Financial losses from climate change can be largely underestimated