Still, according to Joshua Zeichner, Director of Cosmetic and Clinical Research at Mount Sinai School of Medicine’s Department of Dermatology, sometimes what looks like acne simply isn’t.
"Acne is a treatable condition," says Dr. Zeichner. "So if you’re getting spots that won’t go away with over-the-counter treatment, it’s time to see your dermatologist. You want to prevent permanent scarring."
There are many skin conditions that mimic acne, but are different diseases altogether. Recognizing signs that distinguish acne from other conditions can help patients receive appropriate treatment, because traditional acne medicines will not always help all acne-like conditions. Dr. Zeichner outlines three conditions commonly confused as acne.
● Gram Negative Folliculitis
Gram Negative Folliculitis is a bacterial infection of the hair follicle, most commonly occurring in patients on long term antibiotics for acne or rosacea.
"Over time, the oral antibiotics sometimes cause a change in the skin’s normal bacteria, resulting in infection," says Dr. Zeichner. "The bacteria grows in areas that produce oil, such as sweat glands. The most common treatment is medication that reduces oil production."
● Perioral Dermatitis
These itchy red bumps and pus pimples around the mouth are probably a variant of rosacea. It usually occurs in patients who have been using cortisone cream on the face for a long period.
"Perioral dermatitis can improve slowly by discontinuing use of any topical steroids and careful use of other anti-inflammatory medications. Patients will need to find another treatment for whatever issue they were originally using the cortisone cream for," says Dr. Zeichner.
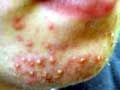
● Pityrosporum Folliculitis
These spots on the chest or the back, which can be itchy, are a rash caused by yeast on the skin. Over 90 percent of patients carry yeast on their skin, but only a small percentage develop this condition. The yeast, called pityrosporum grows in areas of the skin with high oil levels, such as the middle of the chest and back.
"Overgrowth of pityrosporum in the hair follicles can lead to the development of pus pimples," says Dr. Zeichner. "These often do not respond to traditional acne medicines, as they do not treat the yeast. Although difficult to diagnose, the condition can usually be treated with antifungal agents."















Related Items
A victory for peace, pragmatism, and common sense…
New autism therapy may help patients become more self-sufficient
Sukanya Samriddhi Yojana, A decade of transforming lives...