One of the key pillars for achieving the vision of Viksit Bharat by 2047 is ensuring 70 per cent women workforce participation in the country. Women's empowerment is a key driver for national progress, and today India stands to witness a transformative shift.
Now, women are no longer confined to traditional roles; they are breaking barriers and taking charge in shaping the country’s economic future. From rural entrepreneurs to corporate leaders, women are leading India’s march towards Viksit Bharat.
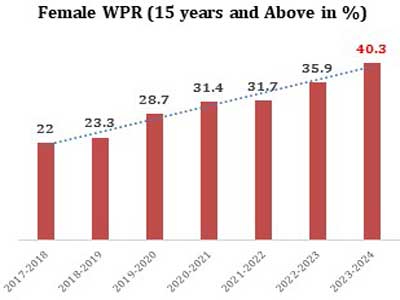
India has witnessed a remarkable increase in the female workforce participation rate, PLFS data shows that the women's employment rate grew from 22 per cent in 2017-18 to 40.3 per cent in 2023-24, while the unemployment rate dropped from 5.6 per cent in 2017-18 to 3.2 per cent in 2023-24, reflecting positive growth in employment opportunities for women. This shift is even more significant in rural India, where female employment has grown by 96 per cent, while urban areas have seen an increase of 43 per cent in employment during the same period.
Reports indicate that the employability of female graduates has also increased from 42 per cent in 2013 to 47.53 per cent in 2024. The employment rate among women with postgraduate education and above has risen from 34.5 per cent in 2017-18 to 40 per cent in 2023-24. As per the India Skills Report 2025, nearly 55 per cent of Indian graduates are expected to be globally employable in 2025, up from 51.2 per cent in 2024.
Additionally, EPFO payroll data further highlights the increasing participation of women in the formal sector. Over the past seven years, 1.56 crore women have joined the formal workforce. Meanwhile, e-Shram, as of August, has recorded over 16.69 crore unorganised women workers’ registrations, providing them access to various social welfare schemes of the Indian government.
PLFS data shows that female self-employment grew by 30 per cent - from 51.9 per cent in 2017-18 to 67.4 per cent in 2023-24, making women truly Atmanirbhar. Gender budgets have increased by 429 per cent in the last decade, rising from ₹0.85 lakh crore in FY 2013-14 to ₹4.49 lakh crore in FY 2025-26. This reflects a paradigm shift from women’s development to women-led development, with a strong focus on employment, employability, entrepreneurship, and welfare.
Programs like Startup India have fostered a thriving ecosystem, with nearly 50 per cent of DPIIT-registered startups having at least one woman director, i.e., 74,410 out of over 1.54 lakh. Today, around two crore women have become Lakhpati Didi. Flagship programs such as Namo Drone Didi, Deendayal Antyodaya Yojana – NRLM are also playing a crucial role in this transformation, equipping them with resources and opportunities needed to drive sustainable progress.
Another important driver of the rise in women's self-employment is PM Mudra Yojana, which is playing a crucial role in financial inclusion, with women receiving 68 per cent of the total MUDRA loans, over 35.38 crore loans worth ₹14.72 lakh crore. Similarly, under PM SVANidhi has empowered street vendors have been empowered, and around 44 per cent of beneficiaries are women under the scheme. These initiatives are driving a new wave of economic self-reliance among women across India.
Additionally, women-led Micro, Small, and Medium Enterprises have also emerged as key drivers of economic expansion, generating over 89 lakh additional jobs for women from FY 21 to FY 23. The share of women-owned proprietary establishments has surged from 17.4 per cent in 2010-11 to 26.2 per cent in 2023-24, and the number of women-led MSMEs has also nearly doubled, growing from 1 crore in 2010-11 to 1.92 crore in 2023-24, highlighting the increasing role of women in shaping India’s economic future.
Women are no longer just participants but the backbone of India's economic growth. Today, women are leading the march toward development.















Related Items
India’s ‘Unique’ Journey as a Republic…
India rises as a ‘Global Medical Travel Destination’
Two pictures from one morning in one country...